INTRODUCTION 🔬
Tuberculosis (TB) remains a significant global health challenge, and isoniazid-resistant TB (Hr-TB) is an increasingly pressing concern, affecting over one million people annually. Despite this, Hr-TB often receives less attention compared to multidrug-resistant TB, particularly in clinical and policy contexts. In China, a country with a high TB burden but low Hr-TB research focus, evidence-based guidance for the treatment and management of Hr-TB remains limited. This study was conducted to address this gap by evaluating the treatment outcomes of Hr-TB patients in Shanghai, a low-endemic region for TB, over a four-year period. By analyzing patient demographics, clinical characteristics, and treatment-related factors, the research aims to provide actionable insights into optimizing therapeutic strategies and improving patient outcomes.
TREATMENT OUTCOMES ANALYSIS 📊
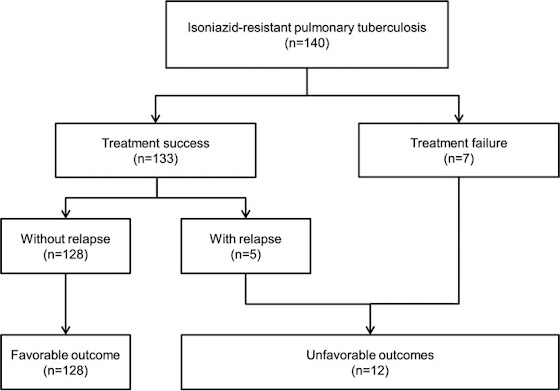
The retrospective review of 664 Hr-TB patients registered between 2018 and 2021 revealed that 12.7% experienced unfavourable treatment outcomes, including treatment failure, default, and death. These findings suggest that while the majority of Hr-TB patients in Shanghai achieved favourable results, a significant minority did not, underlining the complexity of treating drug-resistant TB even in areas with relatively strong healthcare infrastructure. This analysis provides a necessary baseline for understanding the effectiveness of current treatment regimens in real-world settings and highlights the urgent need to refine protocols to reduce the incidence of negative outcomes in this patient population.
REGIMEN COMPOSITION AND FLUOROQUINOLONE USAGE 💊
Only 47.9% of the patients received regimens that included fluoroquinolones, a key component recommended for the treatment of Hr-TB by the World Health Organization. This relatively low utilization rate raises concerns about the adherence to international guidelines and the potential underuse of effective therapeutic agents. The data suggest a disconnect between policy and practice, possibly influenced by local treatment preferences, drug availability, or patient-specific contraindications. The role of fluoroquinolones in improving outcomes for Hr-TB needs further investigation to encourage wider, guideline-based usage across treatment centers.
ADVERSE EVENTS AND TREATMENT INTERRUPTIONS ⚠️
Adverse events were reported in 19.1% of patients, and while most cases were managed without discontinuation, 1.81% ceased treatment entirely due to side effects. Importantly, the incidence of adverse events varied significantly across different regimens (P < 0.001), suggesting that some treatment combinations may pose a higher risk. These findings underscore the critical importance of monitoring and managing drug-related toxicity in Hr-TB treatment to ensure adherence and prevent interruptions, which can contribute to treatment failure and further drug resistance.
IDENTIFIED RISK FACTORS FOR UNFAVOURABLE OUTCOMES 🧬
Multivariable logistic regression analysis identified several risk factors independently associated with unfavourable treatment outcomes. Older age (aOR = 6.13), the use of injectable agents (aOR = 3.75), and extended treatment duration were statistically significant contributors. These insights highlight vulnerable subpopulations within the Hr-TB cohort that may require tailored approaches, including closer monitoring, alternative regimens with fewer side effects, and potential adjustments to treatment duration based on patient response and tolerance.
IMPLICATIONS FOR POLICY AND CLINICAL PRACTICE 🏥
This study provides valuable evidence for healthcare policymakers and clinicians by identifying both the clinical and programmatic challenges in treating Hr-TB in a low-endemic urban setting. The findings call for enhanced diagnostic strategies, better adherence to recommended regimens such as fluoroquinolone-based therapies, and improved patient management to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes. Moreover, incorporating these insights into updated national and local TB control guidelines can help align clinical practice with the evolving evidence base, ultimately improving outcomes for patients with drug-resistant TB.
📌 Visit: https://infectious-diseases-conferences.pencis.com
🏅 Nominate Now: https://jut.li/XWmUe
🏅 Nominate Now: https://jut.li/XWmUe
Hashtags
#Tuberculosis #DrugResistance #IsoniazidResistantTB #HrTB #TBShanghai #PublicHealth #ClinicalOutcomes #Fluoroquinolones #TBResearch #TBPolicy #AntibioticResistance #GlobalHealth #TBChina #TBAdverseEvents #MultivariableAnalysis #TBRegimen #Epidemiology #InfectiousDiseases #TreatmentOptimization #HealthEquity



No comments:
Post a Comment